12th Generation Intel Core i H-Series Mobile Gaming Processors Compared
With Apple stealing the limelight with their M1 Apple silicon chips, the M1 Pro, M1 Max and now the M1 Ultra, it is time for Intel to get some of that love too. As the 11th generation Intel Core-i processors are further sub-divided into different series the 12th generation processors too get the same treatment. This time, there are three, the H-series, the P-series and the U-series. Of these we pick three that are powering today’s laptops for a quick performance comparison.
Over time, more and more processors from the Intel’s 12th generation family will find their way into the laptops but for now, three of these have found their way into gaming laptops, more so than any of the other processors. There is an exception, in that the new Samsung Galaxy Book2 Pro and Pro 360 have started to use the P series processor listed below.
- Intel® Core™ i7-1260P Processor: Samsung Galaxy Book2 Pro 360 13.3, Samsung Galaxy Book2 Pro 15.6,
- Intel® Core™ i5-1240P Processor: Samsung Galaxy Book2 Pro 360 13.3 and 15.6, Samsung Galaxy Book2 Pro 13.3 and 15.6
The three processors from the H series favoured by Gaming Laptop manufacturers are highlighted below:
- Intel® Core™ i7-12450H Processor: ASUS TUF Dash F15
- Intel® Core™ i7-12650H Processor: ASUS TUF Dash F15
- Intel® Core™ i7-12700H Processor: GIGABYTE AERO 5 15.6, MSI GS66 Stealth 15.6, GIGABYTE AORUS 17 XE4, MSI Katana GF66 15.6, MSI Crosshair 15, MSI GE66 Raider 15.6,
- Intel® Core™ i9-12900H Processor: GIGABYTE AERO XE5 16, MSI Crosshair 17, ASUS ROG STRIX SCAR 15, ASUS ROG Zephyrus M16
- Intel® Core™ i9-12900HK Processor: MSI GE76 Raider Deluxe Edition 17.3, MSI Vector GP66 15.6
We take a look at the performance of these processors in the next section.

The H-Series Processors for Gaming
Lets take a closer look at the specifications of these three processors compared to others on Intel’s H-series processor.
12th Gen Intel® Core™ mobile processors redefine multi-core architecture for laptop PCs with an all-new performance hybrid architecture. Built on the new Intel 7nm process, this design breakthrough brings together two types of specialized cores to deliver revolutionary performance and responsiveness. The latest platform technologies, like DDR5 memory support, Thunderbolt™ 4 connectivity and Intel® Wi-Fi 6E (Gig+), elevate your experience even further. Whether you’re a casual multi-tasker, an elite gamer or an imaginative creator, 12th Gen Intel® Core™ mobile processors excel in the areas that matter most.
The Core i9 and Core i7 we will look at all come with 14 cores and 20 thread. They have 6 performance core and 8 efficient cores as well as 24MB Intel Smart Cache. The difference here is one of speed, see table below.
| i9-12900HK | i9-12900H | i7-12800H | i7-12700H | i7-12650H | i5-12600H | i5-12500H | i5-12450H | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processor Cores | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 10 | 12 | 12 | 8 | |
| Processor Threads | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 12 | |
| Number of P-cores | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Number of E-cores | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 4 | |
| Intel® Smart Cache (L3) | 24MB | 24MB | 24MB | 24MB | 24MB | 18MB | 18MB | 12MB | |
| Max Turbo Frequency (GHz)3 up to | P-core | 5 | 5 | 4.8 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.4 |
| E-core | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.7 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | |
| Base Frequency (GHz)3 | P-core | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 2.0 |
| E-core | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 2 | 1.8 | 1.5 | |
| Processor Graphics | 96EU | 96EU | 96EU | 96EU | 64EU | 80EU | 80EU | 48EU | |
| Max Graphics Frequency (GHz) up to | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.2 | |
| Base Power (PL1) | 45W | ||||||||
| Turbo Power (PL2) | 115W | 115W | 115W | 115W | 115W | 95W | 95W | 95W | |
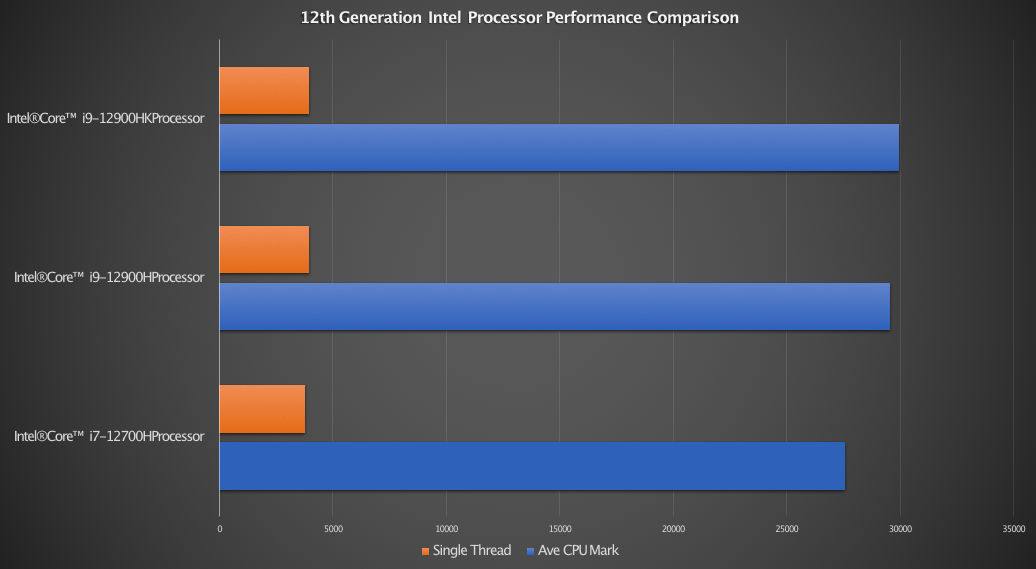
Of the three processors, the most common among them is the Intel Core i7-12700H with more gaming laptops adopting the CPU than the other two. The processor is the first in the line of 14-core processors. Anything below that comes with either an 8-core, 10-core or 12-core. The real test comes from benchmark results. How does it compare to its faster siblings, the Intel Core i9-12900H and Intel Core i9-12900HK. See table below.
| Ave CPU Mark | Single Thread | |
| Intel® Core™ i7-12700H Processor | 27581 | 3757 |
| Intel® Core™ i9-12900H Processor | 29534 | 3967 |
| Intel® Core™ i9-12900HK Processor | 29935 | 3935 |
From the figures above, the Intel Core i9-12900H is 7% faster in the Average CPU Mark and 5.6% faster in single thread performance. If you look at the chart topping Intel Core i9-12900HK, the fastest 12th generation processor is only 8.5% faster in the Average CPU Mark and 4.7% faster in single thread performance when compared to Intel Core i7-12700H. So the question to ask yourself is, is it worth the premium to go for a Core i9 processor as oppose to the Core i7. See graph below.

Other Intel Core-i Mobile Processors Coming Soon
Mainstream processors from Intel, ones that balance performance and efficiency, the P-series or even ones that focus on super long battery life and ultra slim chassis, the U-series are making their way to the shelves albeit slowly. These are highlighted in the table below.
The P-Series Processors
It is still early days and the result samples are still small to have a good idea of the processors performance. These are more mainstream energy efficient mobile processors compared to the H series above. They are better on the battery with base power of 28W and turbo power of 64W which is only around half of 45W and 115W respectively on the H-series processor we looked at above.
| i7-1280P | i7-1270P | i7-1260P | i5-1250P | i5-1240P | i3-1220P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processor Cores | 14 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 10 | |
| Processor Threads | 20 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 12 | |
| Number of P-cores | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | |
| Number of E-cores | 8 | ||||||
| Intel® Smart Cache (L3) | 24MB | 18MB | 18MB | 12MB | 12MB | 12MB | |
| Max Turbo Frequency (GHz)3 up to | P-core | 4.8 | 4.8 | 4.7 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 |
| E-core | 3.6 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | |
| Base Frequency (GHz)3 | P-core | 1.8 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.5 |
| E-core | 1.3 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | |
| Processor Graphics | 96EU | 96EU | 96EU | 80EU | 80EU | 64EU | |
| Max Graphics Frequency (GHz) up to | 1.45 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.1 | |
| Base Power (PL1) | 28W | ||||||
| Turbo Power (PL2) | 64W | ||||||
As we pointed out previous only Samsung Galaxy Book2 Pro and Pro 360 be it 13.3-inch or 15.6-inch adopted these processors.
- Intel® Core™ i7-1260P Processor: Samsung Galaxy Book2 Pro 360 13.3, Samsung Galaxy Book2 Pro 15.6,
- Intel® Core™ i5-1240P Processor: Samsung Galaxy Book2 Pro 360 13.3 and 15.6, Samsung Galaxy Book2 Pro 13.3 and 15.6
The U-Series Processors
The U-series processors are further sub-divided into two categories, the low powered 15W and an even lower 9W. These will be used to power ultra portables, mid-range and ultra budget laptops.
Currently, at the time of writing, the only laptop we are aware of with a processor from this series is the Samsung Galaxy Book 2 360, a convertible 2-in-1 laptop powered by Intel Core i7-1255U processor. The specification is pretty meaty with a generous 16GB memory and 512GB SSD storage. It comes with a 13.3-inch Full HD AMOLED touchscreen panel and will support input with a stylus although the S Pen is sold separately. Elsewhere, you fill find dual speakers that pumps out Dolby Atmos sound, super slim (12.94mm) body and ultra lightweight (1.16kg) design and a chassis that is durable enough to withstand MIL-STD-810G military tests.

15W
| i7-1265U | i7-1255U | i5-1245U | i5-1235U | i3-1215U | Pentium 8505 | Celeron 7305 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processor Cores | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 6 | 5 | 5 | |
| Processor Threads | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 8 | 6 | 6 | |
| Number of P-cores | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Number of E-cores | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Intel® Smart Cache (L3) | 12MB | 12MB | 12MB | 12MB | 10MB | 8MB | 8MB | |
| Max Turbo Frequency (GHz)3 up to | P-core | 4.8 | 4.7 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 | |
| E-core | 3.6 | 3.5 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | ||
| Base Frequency (GHz)3 | P-core | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| E-core | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | |
| Processor Graphics | 96EU | 96EU | 80EU | 80EU | 64EU | 48EU | 48EU | |
| Max Graphics Frequency (GHz) up to | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | |
| Base Power (PL1) | 15W | |||||||
| Turbo Power (PL2) | 55W | |||||||
9W
| i7-1260U | i7-1250U | i5-1240U | i5-1230U | i3-1210U | Pentium
8500 |
Celeron
7300 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processor Cores | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 6 | 5 | 5 | |
| Processor Threads | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 8 | 6 | 5 | |
| Number of P-cores | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Number of E-cores | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Intel® Smart Cache (L3) | 12MB | 12MB | 12MB | 12MB | 10MB | 8MB | 8MB | |
| Max Turbo Frequency (GHz)3 up to | P-core | 4.7 | 4.7 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 | – |
| E-core | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | – | |
| Base Frequency (GHz)3 | P-core | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| E-core | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | |
| Processor Graphics | 96EU | 96EU | 80EU | 80EU | 64EU | 48EU | 48EU | |
| Max Graphics Frequency (GHz) up to | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| Base Power (PL1) | 9W | |||||||
| Turbo Power (PL2) | 29W | |||||||














