Intel Showdown: Pentium Gold 8505 vs. 7505 – The Leap in Budget Computing
Budget computing has a new favourite, the Intel Pentium Gold 8505. Intel’s Pentium Gold processors have long been a staple for those seeking a balance between performance and affordability. The introduction of the Intel Pentium Gold 8505 processor marks a new chapter in this saga, offering enhancements and efficiencies over its predecessor, the Intel Pentium Gold 7505.
This article looks into a comparative analysis of these two processors, highlighting key differences and the potential impact on users’ computing experiences.
Performance and Architecture
The Intel Pentium Gold 8505 processor is built on Intel’s newer architecture Intel Alder Lake-M, which promises improved efficiency and performance capabilities compared to the older architecture Intel Tiger Lake of the Pentium Gold 7505. This generational leap translates into better processing speed, lower power consumption, and an overall smoother computing experience. Users can expect the 8505 to handle daily computing tasks, from web browsing to document editing, with greater ease.
| Intel Pentium Gold 7505 | Intel Pentium Gold 8505 | |
| Physical cores | 2 (Dual-core) | 5 (Penta-Core) |
| Threads | 4 | 6 |
| Base clock speed | 2 GHz | 1.2 GHz |
| Boost clock speed | 3.5 GHz | 4.4 GHz |
| L1 cache | 160 KB | 80K (per core) |
| L2 cache | 2.5 MB | 1.25 MB (per core) |
| L3 cache | 4 MB | 8 MB (shared) |
| Chip lithography | 10 nm SuperFin | Intel 7 nm |
| Maximum core temperature | 100 °C | 100 °C |
| 64 bit support | + | + |
| Unlocked multiplier | No | No |
Benchmark scores from suites like Cinebench R20 or PassMark often reflect the raw processing power of a CPU. From generation to generation, a typical performance uplift of anywhere from 10% to 20% in single-threaded and multi-threaded tasks is to be expected. BUT nothing prepares us for the performance jump in Pentium Gold 8505. The newer architecture, could show performances up to 80% faster in multi-thread averages and 30% in single-threaded tasks compared to the 7505.
| Cores | Threads | TDP (Typ/Up) | Ave CPU Mark | Single Thread | |
| Intel Pentium Gold 8505 | 5 (1P/4E) | 6 | 15W/55W | 9405 | 3319 |
| Intel Pentium Gold 7505 @ 2.00GHz | 2 | 4 | 15W | 5208 | 2266 |
Source: PassMark Software
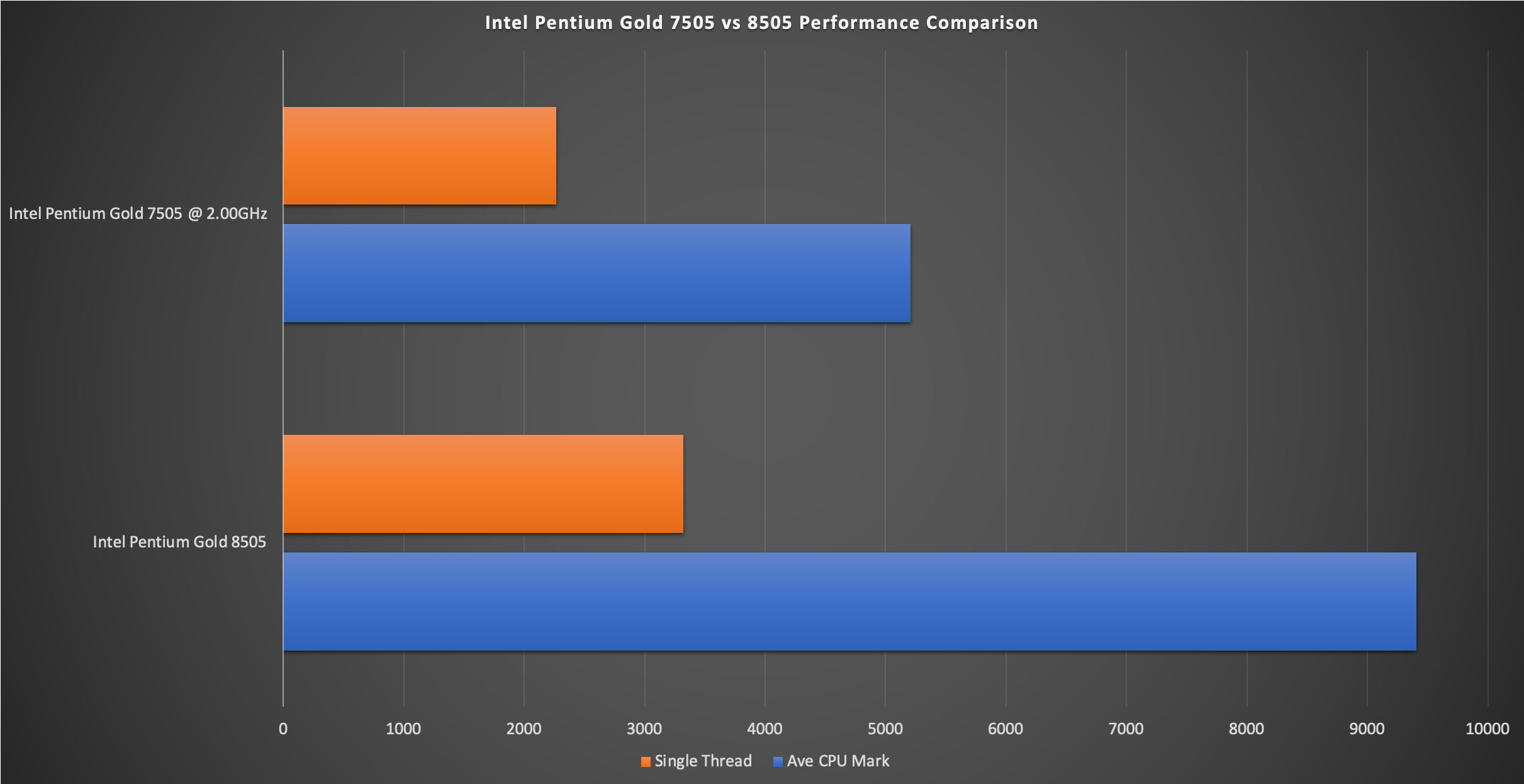
This is all thanks to the new generation Intel Pentium Gold 8505 offering a combination of Performance and Efficient cores and going beyond the dual core in the previous architecture, switching up to 5 cores in total. The performance core also has a higher Turbo speed of 4.4GHz when pushed and double the thread at 2. Still, it manages to stay battery friendly sipping away at 15W power with its low base frequency of 1.2GHz. The other 4 Efficient cores clocks in at 0.9Ghz base frequency and maxes out at 3.3GHz at Turbo. Compare this to the dual core on Pentium Gold 7505. These are capable of 2 threads each for a total of 4 with a base frequency of 2.0GHz and turbo frequency of 3.5GHz. Ultimately, it is the number of cores that counts when it comes to performance.

Core and Thread Count
The Pentium Gold 8505 is a penta-core processor meaning it has 5 CPU cores and is capable of 6 computing threads. On the other hand, the 7505 processors is designed with dual cores and four threads, maintaining a balance that suits everyday computing needs without overextending into the territory of higher-end CPUs that boast more cores for intensive multitasking.
More Cache Memory
The 8505 also benefits from architectural improvements with up to 8MB shared L3 cache and much higher boost clock speed of 4.4GHz compared to 4MB L3 Cache and 3.5GHz boost clock speed on the 7505. The bottom line is both processors are of a different generation even though both uses the 10nm SuperFin manufacturing process.
| Intel Pentium Gold 8505 P Core | Intel Pentium Gold 8505 E Cores | Intel Pentium Gold 7505 | |
| L1 Instruction | L1 Instruction Cache: 1 x 32 KB | Eff. L1 Instruction Cache: 4 x 64 KB | L1 Instruction Cache: 2 x 32 KB |
| L1 Data | L1 Data Cache: 1 x 48 KB | Eff. L1 Data Cache: 4 x 32 KB | L1 Data Cache: 2 x 48 KB |
| L2 Cache | L2 Cache: 1 x 1280 KB | Eff. L2 Cache: 1 x 2048 KB | L2 Cache: 2 x 1280 KB |
| L3 Cache | L3 Cache: 8 MB | L3 Cache: 4 MB |

Search Intel Pentium Gold 8505 Laptop on Amazon
Graphics Performance
Graphics capabilities are a crucial aspect of processor performance, especially for users who engage in light gaming, video streaming, and other graphics-intensive activities. The Intel Pentium Gold 8505 processor comes equipped with Intel’s latest 12th gen integrated graphics technology, offering superior visual performance compared to the 7505’s Intel UHD graphics for 11th Gen processors. This enhancement means smoother video playback, better handling of casual games, and improved support for graphic design applications.
| Intel Pentium Gold 8505 Intel UHD Graphics 12th Gen (48 EU) |
GPU | Item Pentium Gold 7505 Intel UHD Graphics (Tiger Lake G4) |
| 0.20 GHz | GPU frequency | 0.30 GHz |
| 1.10 GHz | GPU (Turbo) | 1.25 GHz |
| 12 | GPU Generation | 11 |
| 10 nm | Technology | 10 nm |
| 3 | Max. displays | 4 |
| 48 | Compute units | 48 |
| 384 | Shader | 384 |
| No | Hardware Raytracing | No |
| No | Frame Generation | No |
| 64 GB | Max. GPU Memory | 32 GB |
| 12 | DirectX Version | 12 |
The Intel UHD Graphics integrated into these processors would also see a generational uplift. While the 12th gen GPU also supports up to 4 displays compared to only 3 on the 11th gen GPU.
Memory and PCIe
Another aspect of the Intel chip that received a boost is its memory bandwidth. While both 8505 and 7505 supports up to 64GB of memory in a dual channel configuration, the maximum bandwidth on Intel Pentium Gold 8505 is 83.2 GB/s while the previous Intel Pentium Gold 7505 max out at 51.2GB/s. There is also an increase in the PCIe channels from 16 to 20 lanes offering again a boost in bandwidth from 15.8GB/s to a whooping 39.4GB/s, more than doubled.
Geekbech 5 benchmark that uses a lot of system memory shows that Intel Pentium Gold 8505 has the upper hand here with single core performance topping at 1550 compared to 1089 on Intel Pentium Gold 7505. That’s 42.3% increase in performance.
As for multicore, the Intel Pentium Gold 8505 scores 4055 while Intel Pentium Gold 7505 only manages 2284, an increase of 77.5%
| Intel Pentium Gold 8505 | Characteristic | Intel Pentium Gold 7505 |
| LPDDR5-5200, LPDDR4X-4266, DDR5-4800, DDR4-3200 | Memory | LPDDR4-3733, DDR4-3200 |
| 64 GB | Max. Memory | 64 GB |
| 2 (Dual Channel) | Memory channels | 2 (Dual Channel) |
| 83.2 GB/s | Max. Bandwidth | 51.2 GB/s |
| No | ECC | No |
| 3.25 MB | L2 Cache | — |
| 8.00 MB | L3 Cache | 4.00 MB |
| 4 | PCIe version | 3 |
| 20 | PCIe lanes | 16 |
| 39.4 GB/s | PCIe Bandwidth | 15.8 GB/s |

Energy Efficiency and Heat Management
With both Intel Pentium Gold 8505 and Intel Pentium Gold 7505 based on 10nm SuperFin manufacturing process and CPU cores operating on different clock speeds for base and turbo, it is hard to tell if the newer 8505 is more efficient and better at heat management.
Typically, newer architecture edges out its predecessor in energy efficiency and heat management. This means not only lower energy consumption, which is beneficial for both the environment and electricity bills, but also less heat generation. But we are talking about the same manufacturing process here. Plus, the newer Intel Pentium Gold 8505 is packing 5 cores vs 2 on the Pentium Gold 7505 albeit with lower base frequencies.
While direct measurements like TDP (Thermal Design Power) remain constant across generations for comparable product tiers, the newer 8505 is definitely in the lead for better performance-per-watt ratios. This means that for the same amount of power, the 8505 delivers more computational capability, which could be indirectly inferred from extended battery life benchmarks in laptops or lower power consumption figures in stress tests.

Search Intel Pentium Gold 8505 Laptop on Amazon
Compatibility and Use Cases
Both processors are compatible with a range of devices, from traditional desktops to all-in-ones and laptops. However, the Pentium Gold 8505, with its improvements in performance and efficiency, is better suited to users looking for a processor capable of keeping up with the increasingly demanding requirements of modern software and operating systems, all while staying within a budget.
For users, these benchmark improvements translate into a noticeably smoother experience in day-to-day tasks. Applications would load faster, multitasking would feel more responsive, and video playback or casual gaming would benefit from the enhanced graphics capabilities. Additionally, the increased efficiency could mean laptops that stay cooler and run longer on a single charge, a critical factor for mobile users.
Conclusion
The Intel Pentium Gold 8505 processor emerges as a clear winner in this comparison, offering notable improvements over the Pentium Gold 7505 in almost every aspect. From enhanced processing power and graphics capabilities to better performance per watt ratio, the 8505 represents a significant step forward for budget-conscious consumers. While the 7505 remains a viable option for basic computing needs, those looking to get the most value for their money, especially with an eye towards future-proofing their investment, would do well to consider the newer Pentium Gold 8505 processor.
While hypothetical benchmark figures serve as a useful guide, the real-world impact of upgrading from a Pentium Gold 7505 to an 8505 processor would be quite tangible for the average user. Whether it’s in quicker application response times, better multimedia performance, or improved battery life, the 8505 offers a compelling upgrade path within the budget computing segment.
At the time of writing there are only a few Intel Pentium Gold 8505 based mobile laptops around and a few more Intel Pentium Gold 7505 based mobile laptops. However, there are quite a few more laptops based Intel Pentium N5030 and N6000 series laptops overall. Also, most offerings are limited to 4GB system memory and up to 128GB eMMC or SSD storage which in our opinion holds back the performance of the Intel Pentium Gold 8505 and 7505. Where possible go for 8B or 16GB RA with 256GB or more SSD storage.










